Images
December 31, 2020 - Tropical Cyclone Chalane
Tweet
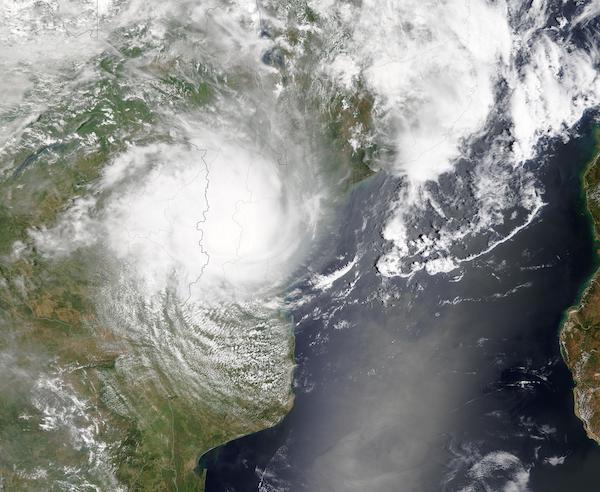
Tropical Storm Chalane made landfall north of Beira City, Sofala Province, Mozambique early on December 30, 2020 carrying rain and moderate wind. Maximum sustained winds at landfall were estimated at 85 km/h (53 mph) with gusts to 120 km/h (75 mph). Early situation reports indicate some damage has been reported, especially in temporary housing sites where people displaced by Cyclone Idai (2019) are living. After landfall, Tropical Storm Chalane travelled inland to Zimbabwe, bringing locally heavy rain as it weakened to a tropical depression.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JWTC) issued its last advisory on the storm on December 30 at 0900 UTC (4:00 a.m. EST). It was located about 23 miles (37 km) north-northwest of Beira, Mozambique and had travelled at 16 mph (26 mph) westward for the six hours prior to the advisory. The report states that Tropical Storm Chalane rapidly eroded after it made landfall. It was carrying winds of about 51 mph (82 km/h). Chalane is forecast to continue to rapidly erode as it crosses the rugged inland terrain, leading to dissipation by December 31.
Tropical Storm Chalane formed roughly a week ago in the Indian Ocean. Prior to striking Mozambique, the storm made landfall in Fenoarivo Atsinanana District, Madagascar, on 27 December with maximum wind gusts of between 40 and 50 km/h (25-31 mph). Chalane quickly weakened to a tropical depression as it moved southwestward across Madagascar before moving into the Mozambique Channel, where it strengthened before striking Mozambique. No significant damage has been reported from Madagascar, although some flooding and local damage did occur.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on board NASA’s Terra satellite acquired a true-color image of Tropical Storm Chalane as it crossed from Mozambique to Zimbabwe on December 30.
Image Facts
Satellite:
Terra
Date Acquired: 12/30/2020
Resolutions:
1km (512.2 KB), 500m (1.7 MB), 250m (4.9 MB)
Bands Used: 1,4,3
Image Credit:
MODIS Land Rapid Response Team, NASA GSFC
Tweet
Tropical Storm Chalane made landfall north of Beira City, Sofala Province, Mozambique early on December 30, 2020 carrying rain and moderate wind. Maximum sustained winds at landfall were estimated at 85 km/h (53 mph) with gusts to 120 km/h (75 mph). Early situation reports indicate some damage has been reported, especially in temporary housing sites where people displaced by Cyclone Idai (2019) are living. After landfall, Tropical Storm Chalane travelled inland to Zimbabwe, bringing locally heavy rain as it weakened to a tropical depression.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JWTC) issued its last advisory on the storm on December 30 at 0900 UTC (4:00 a.m. EST). It was located about 23 miles (37 km) north-northwest of Beira, Mozambique and had travelled at 16 mph (26 mph) westward for the six hours prior to the advisory. The report states that Tropical Storm Chalane rapidly eroded after it made landfall. It was carrying winds of about 51 mph (82 km/h). Chalane is forecast to continue to rapidly erode as it crosses the rugged inland terrain, leading to dissipation by December 31.
Tropical Storm Chalane formed roughly a week ago in the Indian Ocean. Prior to striking Mozambique, the storm made landfall in Fenoarivo Atsinanana District, Madagascar, on 27 December with maximum wind gusts of between 40 and 50 km/h (25-31 mph). Chalane quickly weakened to a tropical depression as it moved southwestward across Madagascar before moving into the Mozambique Channel, where it strengthened before striking Mozambique. No significant damage has been reported from Madagascar, although some flooding and local damage did occur.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on board NASA’s Terra satellite acquired a true-color image of Tropical Storm Chalane as it crossed from Mozambique to Zimbabwe on December 30.
Image Facts
Satellite:
Terra
Date Acquired: 12/30/2020
Resolutions:
1km (512.2 KB), 500m (1.7 MB), 250m (4.9 MB)
Bands Used: 1,4,3
Image Credit:
MODIS Land Rapid Response Team, NASA GSFC