Images
June 2, 2024 - Typhoon Ewiniar
Tweet
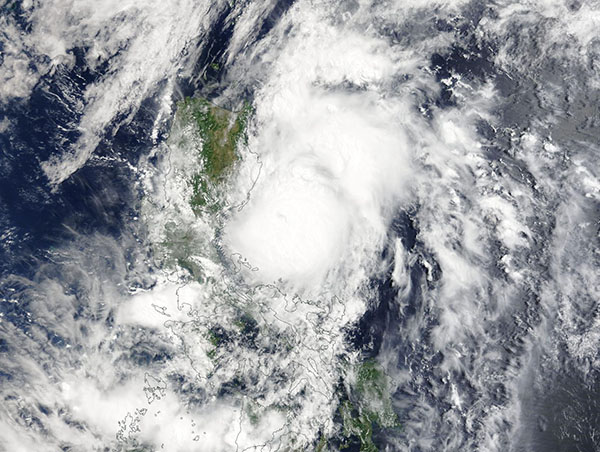
A deadly typhoon was beginning to turn away from the Philippines on May 27, 2024, when the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Terra satellite acquired this true-color image.
At the time the image was captured, Typhoon Ewiniar was carrying maximum sustained winds near or over 100 miles per hour (161 km/h). The storm’s peak strength was 105 miles per hour (169 km/h), or the equivalent of a Category 2 storm on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale. It was located just east of the island of Luzon and was beginning to travel towards the northeast.
Typhoon Ewiniar (also known as Typhoon Aghon) formed over the southern Philippine Sea on May 24 and became the first named storm of the 2024 Pacific Typhoon Season. It moved generally northward over the Philippines, making multiple landfalls. The first was over Homonhon Island and Giporlos, Eastern Samar, then it bounced across Basiao and Dagduyong Islands of Datbalogan, Batuan in Ticao Island, Masbate City, Torrijos, Marinduque, and Lucean, Quezon in Luzon. Ewiniar strengthened through its tour of the Philippine islands, crossing most of them at tropical storm strength before reaching typhoon strength (73 mph or 118 km/h) as it turned away from the island of Luzon.
Although wind speeds were not dramatic as the storm crossed the islands, the wind and rain caused substantial damage. Eight people were reported to have been killed and eight more injured as the storm passed. In addition, ReliefWeb reported that as of May 17, about 19,300 families had been affected by Typhoon Ewiniar in 4 regions, 13 provinces, and 44 cities or municipalities. 5,300 individuals had been displaced, 22 houses were damaged, 7 sections of road were damaged as were one bridge, 57 seaports, and 3 airports. Agricultural damage appears to be extensive.
Image Facts
Satellite:
Terra
Date Acquired: 5/27/2024
Resolutions:
1km (335.8 KB), 500m (1 MB), 250m (2.9 MB)
Bands Used: 1,4,3
Image Credit:
MODIS Land Rapid Response Team, NASA GSFC
Tweet
A deadly typhoon was beginning to turn away from the Philippines on May 27, 2024, when the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Terra satellite acquired this true-color image.
At the time the image was captured, Typhoon Ewiniar was carrying maximum sustained winds near or over 100 miles per hour (161 km/h). The storm’s peak strength was 105 miles per hour (169 km/h), or the equivalent of a Category 2 storm on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale. It was located just east of the island of Luzon and was beginning to travel towards the northeast.
Typhoon Ewiniar (also known as Typhoon Aghon) formed over the southern Philippine Sea on May 24 and became the first named storm of the 2024 Pacific Typhoon Season. It moved generally northward over the Philippines, making multiple landfalls. The first was over Homonhon Island and Giporlos, Eastern Samar, then it bounced across Basiao and Dagduyong Islands of Datbalogan, Batuan in Ticao Island, Masbate City, Torrijos, Marinduque, and Lucean, Quezon in Luzon. Ewiniar strengthened through its tour of the Philippine islands, crossing most of them at tropical storm strength before reaching typhoon strength (73 mph or 118 km/h) as it turned away from the island of Luzon.
Although wind speeds were not dramatic as the storm crossed the islands, the wind and rain caused substantial damage. Eight people were reported to have been killed and eight more injured as the storm passed. In addition, ReliefWeb reported that as of May 17, about 19,300 families had been affected by Typhoon Ewiniar in 4 regions, 13 provinces, and 44 cities or municipalities. 5,300 individuals had been displaced, 22 houses were damaged, 7 sections of road were damaged as were one bridge, 57 seaports, and 3 airports. Agricultural damage appears to be extensive.
Image Facts
Satellite:
Terra
Date Acquired: 5/27/2024
Resolutions:
1km (335.8 KB), 500m (1 MB), 250m (2.9 MB)
Bands Used: 1,4,3
Image Credit:
MODIS Land Rapid Response Team, NASA GSFC